Trendsetting Technology
HAL Therapy
What is a HAL® Exoskeleton?
An exoskeleton is fitted to the outside of the body and gives the wearer additional functional support. The exoskeletons used at the WALK AGAIN Center are made by the Japanese manufacturer Cyberdyne and are made of special light yet sturdy plastic and are known under the name Hybrid Assistive Limb or, for short, HAL®.

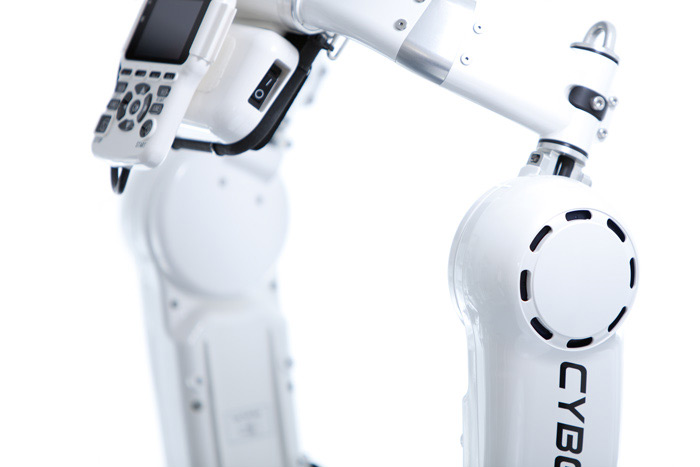
HAL® Therapy: the principle
The robotic suit HAL® is the only approved system of its kind that traps the electrical signals of the brain via the skin surface of the lower limbs and supports them in a motorized manner. The movement is thus a controlled activity deliberately desired by the patient. The positive feedback is sent back from muscles to the brain. During the rehabilitation period using HAL® Therapy the musculature gets built up, the walking pattern improves significantly, becomes safer an walking aids can be reduced.
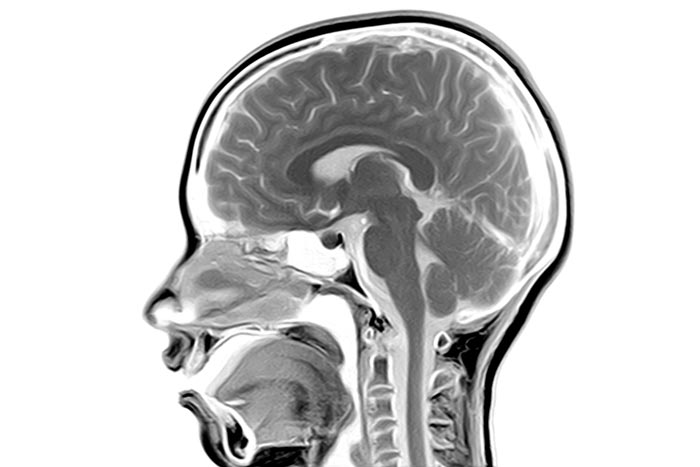
Neuromuscular Feedback
During the HAL® Therapy, impulses from the leg muscles are sent back to the brain. In this manner, a so called neuromuscular feedback is created that causes activation of the cerebral area responsible. The overall condition improves considerably.

Broad Spectrum
Because HAL® exoskeletons compensate for the missing power of the legs, the HAL® Therapy is aimed at a wide group of patients with walking disabilities, who still have some residual functions in their legs since the patient can only steer the robot, if neural impulses on the surface of the skin can be intercepted. The Hybrid Assistive Limb can be used, under certain circumstances, in the rehabilitation of the following conditions:
Results of HAL® Therapy
For example patients with spinal cord injury normally train with the system for 12 weeks, 5 times per week. During this rehab period using HAL® exoskeleton, many key treatment goals can be achieved. For example, the leg muscles are built up, gait is improved significantly and feels steadier.
Scientific studies have shown the following additional improvements:
- Increased walking speed
- Reduced need for medical aids
- Improved skin sensation
- Reduction of spasticity
- Reduction in neuropathic pain
- Strengthening of the muscles
- Stimulation of the affected brain regions

